
Health Care- The health care industry is in the midst of a revolutionary transformation. From the integration of advanced technologies to a renewed focus on patient-centered care, these innovations are leading to more efficient, equitable, and effective health care systems. These emerging trends are not only changing how health care is delivered but also improving the quality of life for individuals worldwide. As we move toward a future where health care is more personalized, accessible, and comprehensive, several key trends are shaping the way forward.
1. Personalized Medicine: A Tailored Approach to Treatment
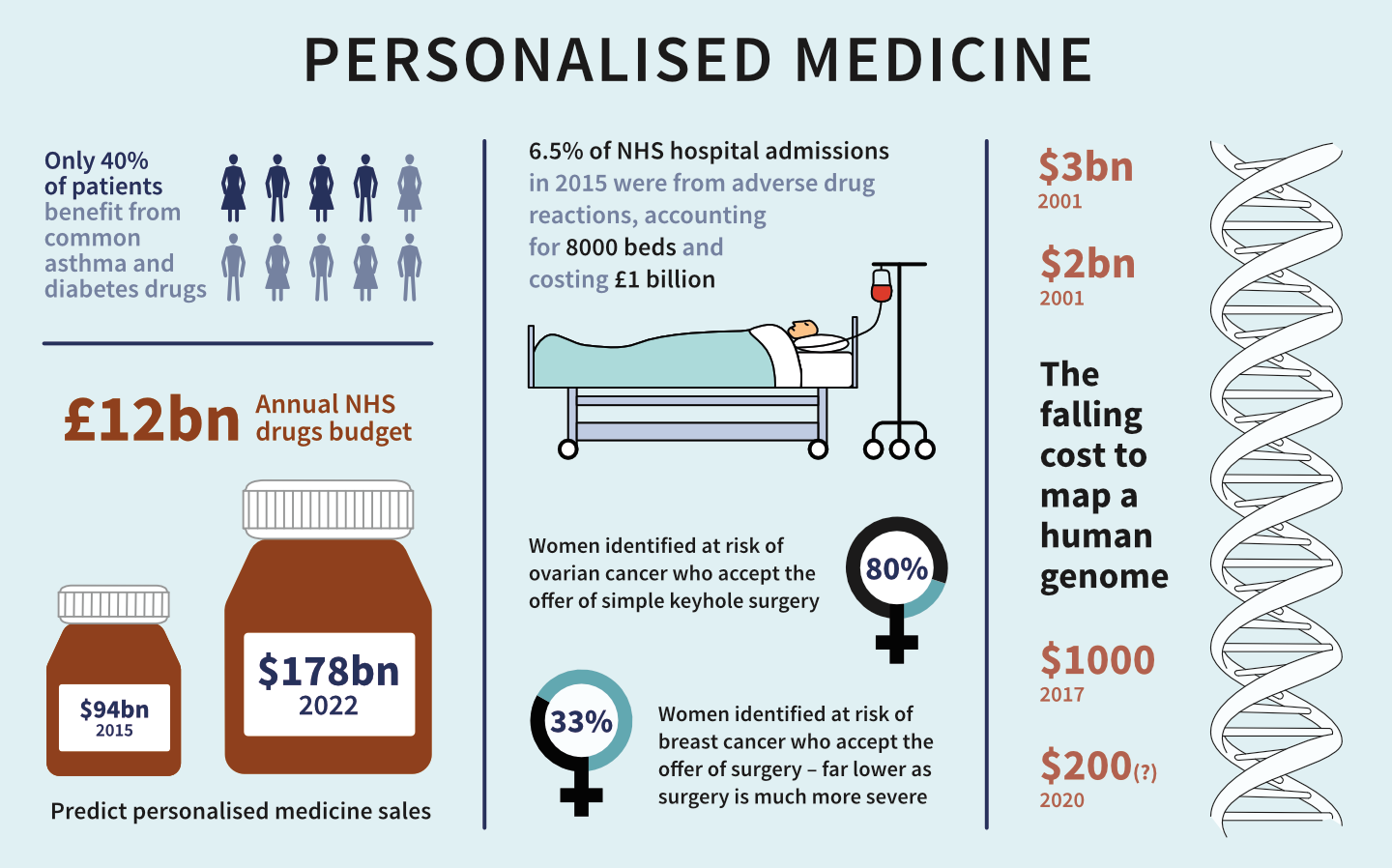
Redefining the Therapeutic Landscape
In the evolving arena of modern health care, 1. Personalized Medicine: A Tailored Approach to Treatment represents a pivotal advancement. Rather than adhering to the antiquated “one-size-fits-all” paradigm, personalized medicine champions individualized therapy based on a person’s genetic blueprint, environment, and lifestyle. This nuanced approach is redefining treatment efficacy, minimizing adverse drug reactions, and elevating health outcomes to unprecedented levels.
The Genomic Revolution
At the heart of personalized medicine lies the genomic revolution. Through next-generation sequencing and genome mapping, clinicians now gain insight into the genetic idiosyncrasies of each patient. These insights unravel predispositions to diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and rare genetic syndromes—facilitating early detection and targeted prevention.
For instance, pharmacogenomics, a subfield of personalized medicine, evaluates how genes influence drug responses. By analyzing genetic markers, clinicians can prescribe medications that synchronize with a patient’s metabolic profile, thereby optimizing therapeutic efficacy and reducing the trial-and-error phase of drug selection.
Beyond Genetics: Lifestyle and Environment
While genetics provides the blueprint, it is the interplay of lifestyle and environmental exposures that complete the picture. Dietary habits, physical activity, stress levels, sleep patterns, and even geographic factors all influence health trajectories. Personalized medicine integrates these variables to create a truly bespoke care plan—one that acknowledges the individuality of human physiology and lived experience.
Nutrigenomics, another emerging discipline, exemplifies this integration. It explores how nutrients affect gene expression and how genetic variants affect nutrient metabolism. The result is custom-tailored nutrition plans that not only manage disease but also enhance overall vitality.
Data-Driven Precision
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are catalyzing this medical metamorphosis. Advanced algorithms process terabytes of data from electronic health records, wearable devices, lab reports, and genetic sequencing. These insights empower clinicians with predictive analytics—enabling early intervention, real-time monitoring, and dynamic treatment adjustments based on patient response.
Moreover, mobile health apps and digital biomarkers allow patients to participate actively in their treatment journey. This fosters a new era of participatory medicine—where individuals are co-architects of their wellness rather than passive recipients of care.
Clinical Impact and Future Prospects
From oncology to psychiatry, personalized medicine is making a seismic impact across disciplines. In cancer care, tumor profiling enables oncologists to target specific mutations with precision therapies, improving survival rates and reducing toxicity. In mental health, personalized pharmacotherapy is refining the treatment of depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia based on genetic and biochemical profiles.
Looking ahead, the integration of personalized medicine into mainstream health systems holds transformative potential. As ethical frameworks, data privacy measures, and equitable access improve, personalized medicine is poised to become the cornerstone of 21st-century care.
1. Personalized Medicine: A Tailored Approach to Treatment is not merely a trend—it is a fundamental shift in the philosophy of care. It embraces complexity, honors individuality, and leverages technology to deliver smarter, safer, and more effective health solutions. In an age where precision matters, personalized medicine is the beacon guiding us toward truly individualized healing.
2. Telemedicine: Revolutionizing Access to Health Care

Breaking Barriers with Digital Healing
2. Telemedicine: Revolutionizing Access to Health Care marks a defining shift in how medical services are delivered in the modern age. Gone are the days when geographical remoteness or time constraints acted as insurmountable obstacles to receiving medical care. Through telemedicine, patients and providers are now connected across vast distances via secure digital platforms, fostering continuity, convenience, and consistency in health management.
The Rise of Virtual Consultations
At the core of telemedicine is the virtual consultation—an innovation that blends clinical expertise with digital agility. Through high-definition video conferencing, secure messaging, and real-time diagnostics, patients can now engage with physicians without leaving their homes. This not only eliminates travel burdens but also expedites early intervention, especially for chronic conditions requiring regular monitoring.
In underserved or rural regions, where medical specialists are scarce, telemedicine bridges the accessibility gap. A remote community can consult a cardiologist or endocrinologist hundreds of miles away with just a few clicks, dramatically improving prognosis and reducing delays in care.
Beyond Primary Care: A Broadening Spectrum
Telemedicine is not confined to general consultations. Its reach now extends to dermatology, psychiatry, radiology, oncology, and even post-operative rehabilitation. Dermatologists assess skin lesions via image uploads; therapists provide mental health support through video sessions; radiologists interpret scans from distant imaging centers.
The growing adoption of remote monitoring devices—such as smart glucometers, blood pressure cuffs, and wearable ECGs—enables clinicians to gather vital signs continuously, even outside hospital walls. These tools ensure that treatment plans are informed by real-time data rather than sporadic check-ups.
Efficiency Meets Affordability
Telemedicine reduces the administrative load on health care systems. Fewer in-person visits mean lower overhead costs, optimized clinician schedules, and shorter waiting times. Patients, in turn, save on travel expenses, child care arrangements, and time off work. For many, especially those managing chronic illnesses, this model alleviates both financial and logistical burdens.
Moreover, asynchronous telemedicine—where patients send messages, images, or forms to be reviewed later—offers flexibility for both parties. It decentralizes care while maintaining clinical oversight, allowing for scalable service delivery without compromising quality.
Safety in a Post-Pandemic World
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated telemedicine’s ascent from convenience to necessity. As clinics limited in-person visits, digital health care emerged as a lifeline. Even in the aftermath, telemedicine remains vital for infection control, reducing exposure risks for immunocompromised individuals or those in quarantine.
The technology also supports population health initiatives, such as virtual screening during outbreaks, remote vaccination education, and chronic disease management programs—enhancing overall public health resilience.
The Road Ahead
As artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and 5G networks continue to evolve, telemedicine will become even more immersive and predictive. Voice recognition, virtual reality-assisted therapies, and AI-driven diagnostic tools will refine remote care to a level once unimaginable.
2. Telemedicine: Revolutionizing Access to Health Care is more than a digital upgrade—it is a paradigm shift. By dismantling physical, economic, and temporal barriers, telemedicine redefines health care delivery for the 21st century. It empowers patients, enhances provider reach, and sets the stage for a more agile, inclusive, and responsive health care ecosystem.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy

Precision in the Digital Era
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy represents a transformative leap in modern health care. No longer relegated to science fiction, AI and ML are now pivotal in refining diagnostics, offering clinicians a powerful toolkit for interpreting complex data with unmatched precision. This convergence of computational prowess and clinical insight is redefining the very architecture of patient care.
Pattern Recognition Beyond Human Capability
At the core of diagnostic innovation lies machine learning’s unparalleled pattern recognition. Algorithms trained on vast datasets can detect anomalies in medical imaging—such as tumors, fractures, or hemorrhages—with a level of consistency that even the most experienced specialists may struggle to match. These systems learn continuously, analyzing thousands of images, lab results, and patient records to improve their predictive capabilities over time.
AI-driven diagnostic tools now assist in radiology, pathology, cardiology, and oncology, where early detection often determines the trajectory of treatment outcomes. In mammography, for example, AI algorithms can flag microcalcifications or asymmetries that may suggest early-stage breast cancer—often before they’re visible to the human eye.
Speed Meets Accuracy
Speed is another critical advantage. Traditional diagnostic processes can take days—sometimes weeks—depending on complexity and backlog. AI shortens this window significantly. In emergency settings, this acceleration can be life-saving. Algorithms can triage CT scans or flag critical findings in seconds, allowing physicians to prioritize care with greater urgency and confidence.
AI-enhanced diagnostics also reduce false positives and negatives. By synthesizing multi-modal data—like imaging, genomics, and patient history—AI systems provide a holistic view of the patient. This integrative approach limits diagnostic blind spots and fosters more nuanced clinical decisions.
The Role of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing plays a crucial role in mining unstructured clinical data. Patient records, physician notes, and research literature are often written in freeform language. NLP algorithms can extract relevant insights, identify risk factors, and cross-reference findings with current guidelines or medical research. This textual analysis supports more informed and evidence-based diagnoses.
For example, an AI model might identify a correlation between seemingly minor symptoms and a rare disease by comparing the case to global health databases in real-time—something impractical for any one practitioner.
Ethical Intelligence and Oversight
Despite its promise, the integration of AI in diagnostics necessitates ethical vigilance. Algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation, and data privacy are paramount. Medical AI must be interpretable, allowing clinicians to understand how conclusions are reached. It is not a replacement for human judgment, but a sophisticated augmentation.
Regulatory bodies and institutional frameworks are evolving to ensure that AI tools meet stringent safety and efficacy standards. The goal is a synergistic model where machine intelligence complements human empathy and expertise.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy marks a pivotal evolution in health care excellence. Through intelligent data synthesis, real-time analysis, and consistent accuracy, AI and ML are shaping a future where diagnoses are not only faster but profoundly more reliable. This digital transformation heralds a new era—one defined by precision medicine, individualized care, and amplified clinical outcomes.
4. Health and Wellness Integration: A Holistic Approach to Well-Being
Reimagining the Spectrum of Care
4. Health and Wellness Integration: A Holistic Approach to Well-Being signifies a profound shift from reactive treatment to proactive lifestyle optimization. This integrative philosophy bridges conventional medicine with complementary therapies, focusing on the synergy between body, mind, and environment. In an age where stress-related disorders and chronic diseases are rampant, adopting a holistic approach is not a luxury—it is a necessity.
Beyond the Absence of Disease
True wellness transcends the mere absence of pathology. It encompasses vitality, resilience, emotional balance, and cognitive clarity. Holistic care recognizes that well-being is dynamic and multifactorial. It invites a deeper exploration into personal habits, nutrition, sleep, relationships, and spiritual alignment—offering a panoramic view of what it means to thrive.
Medical professionals and wellness practitioners increasingly collaborate to create integrative care plans. This might include a fusion of functional medicine, nutritional therapy, mindfulness practices, acupuncture, and fitness programs—all tailored to the individual’s constitution, lifestyle, and goals.
Personalized Preventive Strategies
Preventive medicine plays a pivotal role in health and wellness integration. Through biometric screenings, lifestyle assessments, and genomic profiling, practitioners can identify predispositions to disease and intervene early. Nutritional adjustments, stress-reduction strategies, and customized fitness regimens become frontline defenses rather than afterthoughts.
For example, a patient with a family history of cardiovascular disease may benefit not only from cholesterol monitoring but also from stress-relieving practices like yoga or forest bathing, anti-inflammatory diets, and resilience coaching. It’s a paradigm shift that empowers individuals to become custodians of their own health narratives.
Mind-Body Synchronization
The mind-body connection is not abstract—it is measurable and powerful. Psychological stress, when unregulated, manifests physiologically. Elevated cortisol levels, poor sleep, digestive disruptions, and immune suppression are common indicators. By incorporating meditation, breathwork, and cognitive-behavioral therapy into wellness plans, practitioners help patients mitigate these somatic effects.
Holistic frameworks encourage emotional fluency, teaching individuals to process trauma, nurture relationships, and cultivate purpose. These elements are no longer seen as peripheral but as central components of long-term health.
Community and Environmental Dimensions
Well-being does not occur in isolation. Environmental design, community belonging, and even digital hygiene affect individual health outcomes. Health and wellness integration therefore extends beyond the clinical setting into homes, workplaces, and social circles.
Access to green spaces, ergonomic design, supportive communities, and clean nutrition are increasingly recognized as core pillars of sustainable wellness. These external variables must align with internal efforts to create harmony and enduring health.
4. Health and Wellness Integration: A Holistic Approach to Well-Being reframes the future of health care as collaborative, preventative, and person-centered. It urges a symphonic approach to well-being—one that harmonizes modern science with ancient wisdom, individual biology with communal health, and physical healing with emotional restoration. The result is a more complete, empowered, and vibrant model of living well.
5. Precision Public Health: Targeted Interventions for Communities
Precision public health is an emerging trend that takes personalized medicine principles and applies them on a larger, community-wide scale. Rather than a broad, one-size-fits-all approach, precision public health uses data analytics to target specific populations based on their unique health risks, environmental factors, and behaviors.
By leveraging genomic data, social determinants of health, and environmental factors, health organizations can identify at-risk populations and design tailored interventions. These interventions could range from targeted vaccination campaigns to personalized disease prevention programs. The goal is to reduce health disparities and improve outcomes for underserved populations by delivering interventions that are most likely to have the greatest impact.
In addition, precision public health is being used to monitor and address the effects of climate change on public health, such as increased risks of respiratory diseases due to air pollution. With its data-driven approach, this trend holds the promise of a more equitable and effective public health strategy.
6. Sustainability in Health Care: Greener Practices for a Healthier Future
As the global population grows and resources become more limited, sustainability has become an important focus in the health care industry. From reducing waste to minimizing energy consumption, health care systems are increasingly adopting environmentally-friendly practices to ensure long-term sustainability.
Hospitals and clinics are implementing greener practices by using energy-efficient technologies, reducing carbon emissions, and incorporating sustainable building materials. Furthermore, the health care sector is shifting towards waste reduction, with many institutions adopting policies to reduce single-use plastics, improve recycling programs, and promote environmentally-friendly disposal of medical waste.
Sustainability efforts also extend to the food and pharmaceuticals sectors, with health care organizations sourcing more sustainable and ethical products. This holistic focus on sustainability not only helps protect the environment but also contributes to the overall health of the community by reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and promoting cleaner, healthier living conditions.
These trends represent just a few of the positive changes that are shaping the future of health care. As technology advances and society embraces a more personalized, holistic approach to well-being, the promise of better health outcomes for all becomes more tangible. Through innovation and collaboration, the future of health care holds the potential to be more inclusive, accessible, and effective than ever before.